In a presentation at the Dortmund Conference (dokorp) 2025 “Reasons for planning in time of multiple crisis”, Katharina Holec, Laura Mark and Tobias Escher presented further selected recommendations for dealing with planning conflicts in the context of the transport transition. The presentation arose from the ongoing work on recommendations for action, which was developed by the CIMT research group as a synthesis of the various strands of research and in cooperation with practitioners.
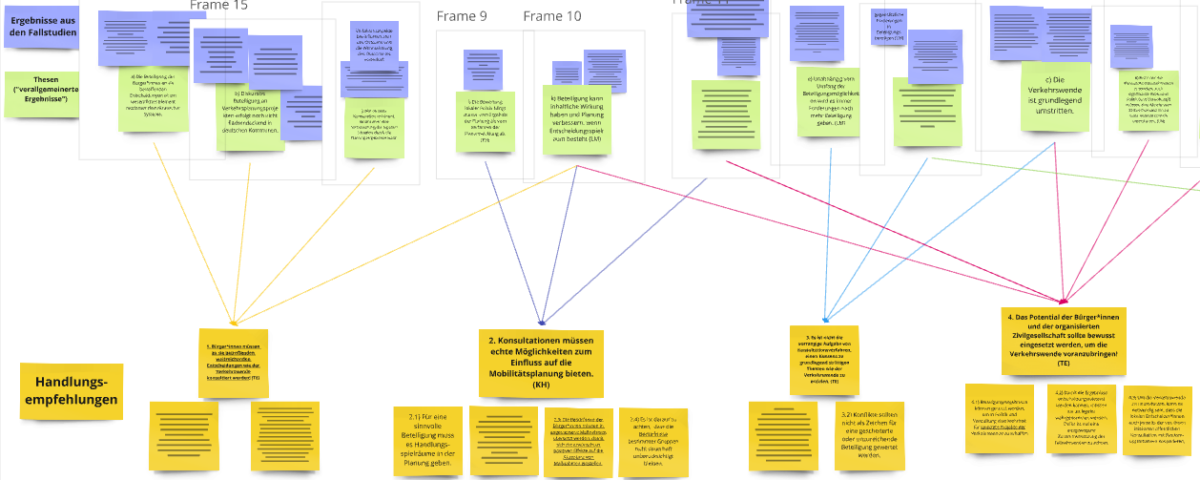
These recommendations are derived from various research findings from the CIMT project. They are based on quantitative data from surveys of more than 2,000 people and qualitative data from more than 20 interviews on various mobility planning processes in three German cities, as well as a quantitative analysis of the participation landscape in Germany based on an extensive database of over 350 transport-related participation processes that we have built up. Following feedback from practitioners, they were revised and put into a coherent form.
Recommendations
For the presentation, the following two recommendations were selected from those developed to date and presented for discussion:
It is not the primary task of consultation processes to reach a consensus on fundamentally controversial issues such as the mobility transition.
Compared to the presentation at the CMUS conference in Aalborg, this recommendation was slightly adapted and reformulated in the process of developing the recommendations for action, so that consensus is still not seen as the primary task of consultation procedures, but can at least be sought as a partial aspect. Furthermore, it is emphasized that the transport transition is fundamentally controversial. The derivation of the recommendations for action can be found in the contribution to the Mobilities Controversies Conference in Aalborg 2024.
The results of the consultation must be supplemented by other perspectives in order to arrive at a balanced decision in the interests of the mobility transition!
Here, too, the wording was slightly adapted after discussion with practitioners. The wording was changed primarily to make it clear once again that decisions should primarily be made in the interests of the mobility transition and that these should also be balanced for different socio-economic groups.
Presentation and publication
We are currently working on a compilation of these and other empirically based recommendations for the use of participation in the mobility transition.